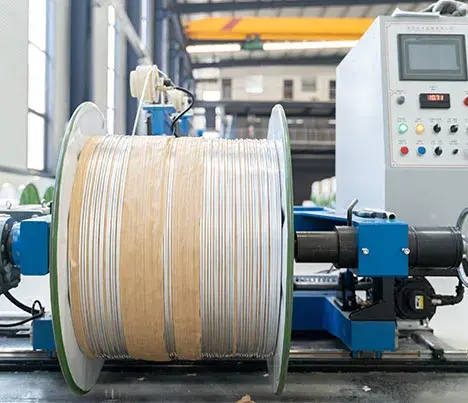
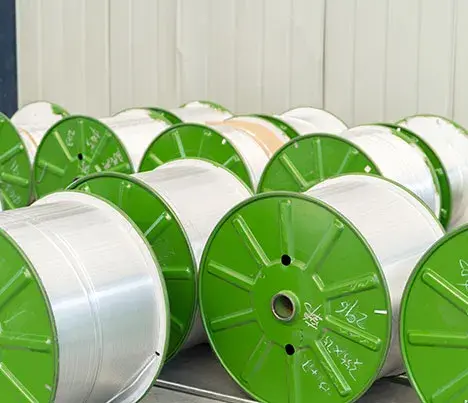
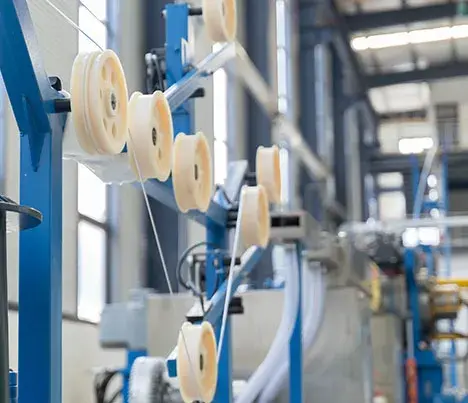
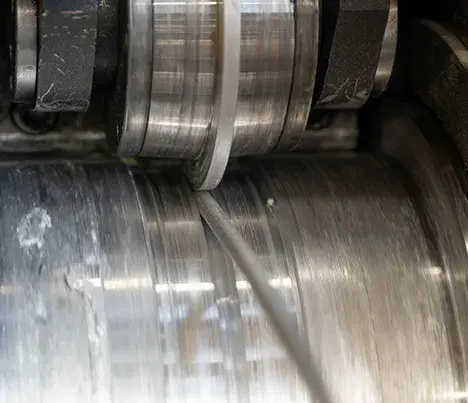
Introduction
Aluminum alloy wire is a metal wire product with a tensile strength σb (MPa) ≥ 180. Aluminum alloy wires are used in large-span high-voltage overhead transmission lines, and steel-cored aluminum alloy stranded wires are the most used. The production and application technology of this type of wire is basically mature, but its heat resistance and corrosion resistance are relatively weak. The transmission capacity of the line is limited to a certain extent.
Aluminum / aluminum combined with various percentages of other metals such as copper, manganese, magnesium, and chromium form the aluminium / aluminum alloys. In most cases aluminium / aluminum 2000 series alloys in the form of sheet are clad with a high-purity aluminium / aluminum 6000 or 7000 series alloy to provide physical and electrolytic protection to the key material, and thereby increasing resistance to corrosion. Aluminium / aluminum 2018 alloy is a heat treatable wrought alloy. The following datasheet will provide more details about aluminium / aluminum 2117 alloy.