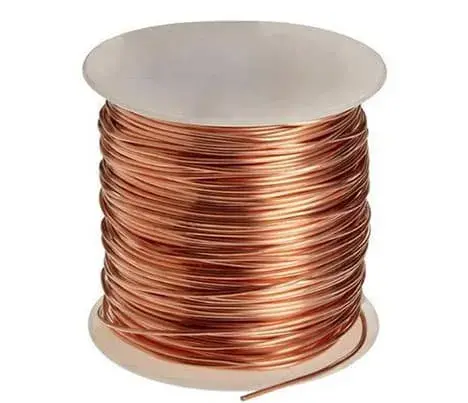
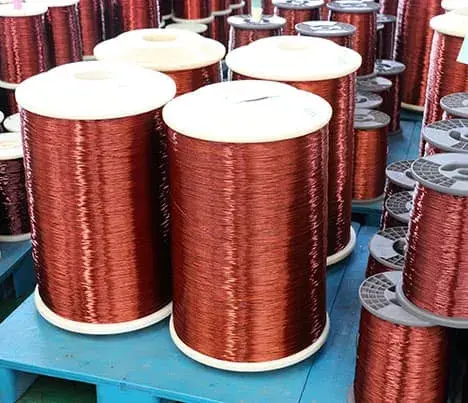
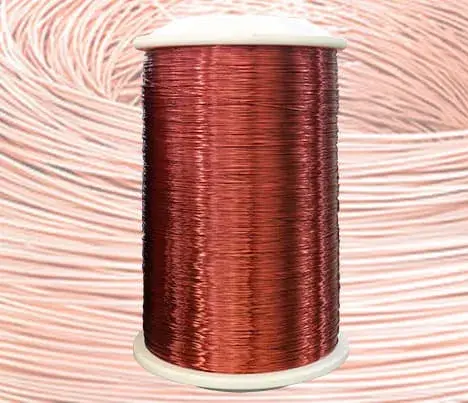
What's the copper conductor?
Pure copper is a soft metal, the surface is red-orange with metallic luster when it is just cut, and the element is purple-red. It has good ductility, high thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, so it is the most commonly used material in cables and electrical and electronic components. It can also be used as a building material and can be composed of many kinds of alloys. Copper alloys have excellent mechanical properties and low resistivity, the most important of which are bronze and brass. In addition, copper is also a durable metal that can be recycled many times without compromising its mechanical properties.
Copper is a purple-red lustrous metal with a density of 8.92 g/cm3. Melting point 1083.4 ℃, boiling point 2567 ℃. Has good ductility. Good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Copper is essential to all living organisms as a trace dietary mineral because it is a key constituent of the respiratory enzyme complex cytochrome c oxidase. In molluscs and crustaceans, copper is a constituent of the blood pigment hemocyanin, replaced by the iron-complexed hemoglobin in fish and other vertebrates. In humans, copper is found mainly in the liver, muscle, and bone. The adult body contains between 1.4 and 2.1 mg of copper per kilogram of body weight.