Fully Insulated (FIW) Non-defective Enameled Round Copper Wire
- Insulation Performance
- Mechanical Properties
- Thermal Performance
- Electrical Properties
- Environmental Adaptability
- Dimensions
- Electrical Resistance
- Elongation at Break
- Springiness
- Mandrel winding test
- Heat shock
- Breakdown voltage
- Transformers: used for high-efficiency, low-loss power transformer windings.
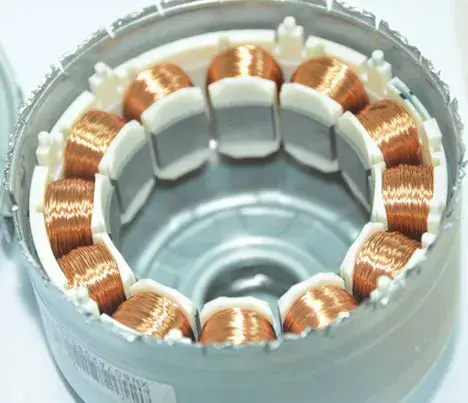
- Motors: used in various motors to improve insulation performance and durability.
- Reactors: used for reactor windings in industrial and power systems to ensure high reliability.
- Electronic equipment: used in high-demand electronic components and circuits, such as sensors, relays, etc.

IEC 60317-0-7 is an international standard for fully insulated (FIW) non-defective enameled round copper wire. This standard specifies in detail the manufacturing requirements, performance tests and application areas of these wires to ensure their reliability and safety in electrical and electronic equipment.

Standard Overview
IEC 60317-0-7 standard provides comprehensive technical requirements for fully insulated (FIW) non-defective enameled round copper wire. These requirements cover the mechanical properties, electrical properties and environmental adaptability of the wire to ensure excellent performance under various conditions of use.
Main specifications
Fully insulated (FIW) enameled wire emphasizes the integrity of the insulation layer and requires no insulation defects (such as pinholes, bubbles, etc.). This ensures that the wire has excellent insulation performance under high voltage conditions to prevent current leakage and short circuits.
—Pinhole test: The insulation layer must undergo a rigorous pinhole test to ensure that there are no tiny defects. For example, the standard stipulates that the number of pinholes in enameled wire per 100 meters of length should be zero.
—Dielectric strength: The insulation layer should be able to withstand high voltage without being broken down, and the dielectric strength is usually required to reach 5000 V/mm or more.
In terms of mechanical properties, IEC 60317-0-7 requires the wire to have high strength and ductility to ensure reliability during processing and use.
—Tensile strength: The wire must have sufficient tensile strength, usually above 200 N/mm², to withstand tensile and bending stresses.
—Ductility: The enameled wire needs to have good ductility, and the elongation is usually required to reach more than 20% to ensure that it will not break during winding and installation.
Fully insulated enameled wire must be able to work stably in high temperature environments without performance degradation.
—Thermal grade: The standard specifies different thermal grades (such as 130, 155, 180, etc.), which indicate that the wire can work for a long time at the corresponding temperature without significant aging.
—Thermal shock test: The wire must pass the thermal shock test, such as keeping it at 200°C for 72 hours, and the insulation layer must not crack or peel off.
In addition to insulation performance, IEC 60317-0-7 also specifies the conductivity and resistance requirements of enameled wire to ensure that it has low loss and high efficiency when transmitting current.
—Conductivity: The conductivity of the wire must meet the conductivity of international standard copper, usually requiring 58 MS/m or more.
—Resistance: The resistivity of the wire should be within the specified range to ensure that no excessive heat is generated under high load.
IEC 60317-0-7 also specifies the adaptability test of enameled wire under different environmental conditions, including moisture resistance, chemical resistance and weather resistance.
—Moisture resistance: The wire must pass the high humidity environment test to ensure that there is no performance degradation under humid conditions.
—Chemical resistance: The enameled wire must be able to withstand certain chemical corrosion, such as acids, alkalis and solvents, to ensure performance in complex industrial environments.
—Weather resistance: The standard also requires that the wire remain stable under UV and other climatic conditions without significant aging.
Specific Requirements for FIW
Dimensions of enameled wires for grade FIW 3,5,7,9
| Nominal
conductor diameter |
Conductor
tolerance |
Minimum overall diameter
mm |
Maximum overall diameter
mm |
||||||
| mm | amm | Grade
of FIW 3 |
Grade
of FIW 5 |
Grade
of FIW 7 |
Grade
of FIW 9 |
Grade
of FIW 3 |
Grade
of FIW 5 |
Grade of
FIW 7 |
Grade of
FIW 9 |
| 040.0
0,045 0,050 0.056 0,063 |
0,055
0,062 0,067 0.075 0,084 |
0.070
0.079 0.084 660.0 0.103 |
0600
0,101 0,106 0,117 0.129 |
0.058
0,066 0.072 0,081 0600 |
0.079
0.089 960.0 0,104 0,115 |
660.0
0,111 0.116 0.128 0,141 |
|||
| 0,071
0,080 0600 0,100 0,112 |
0,003
0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 |
0.092
0,102 0,114 0,126 0,140 |
0,111
0.123 0,135 0,149 0,165 |
0,137
0,151 0,163 0,181 0.199 |
0,163
0,179 0,191 0.213 0,233 |
0,098
0,108 0.120 0,132 0,147 |
0.123
0.136 0,148 0,164 0,181 |
0.149
0,164 0.176 0.196 0,215 |
0,175
0.192 0,204 0,228 0,249 |
| 0.125
0,140 0,160 0.180 0,200 |
0.003
0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 |
0.155
0,172 0.195 0,218 0,240 |
0,182
0,202 0.228 0,254 0.278 |
0,218
0,242 0,272 0,302 0,328 |
0,254
0,282 0,316 0,350 0,378 |
0,163
0,181 0.205 0,229 0,252 |
0,199
0,221 0,249 0,277 0,302 |
0,235
0,261 0.293 0.325 0,352 |
0,271
0,301 0.337 0,373 0,402 |
| 0,224
0,250 0,280 0,315 0,355 |
0.003
0,004 0,004 $00.0 0,004 |
0,267
0,298 0,330 0,368 0,412 |
0,308
0,343 0,377 0,416 0,460 |
0,362
0,403 0,439 0.478 0,522 |
0,416
0,463 0,501 0,540 0,584 |
0,280
0,312 0,345 0,384 0,428 |
0,334
0,372 0,407 0,446 0,490 |
0,388
0,432 0,469 0.508 0,552 |
0,442
0,492 0,531 0,570 0,614 |
| 0,400
0,450 0,500 0,560 0,630 |
0.005
0,005 0.005 9000 900 0 |
0,460
0,514 0,567 0,631 0,705 |
0,510
0,565 0.629 0,695 0,770 |
0,572
0,627 0,711 0,777 0.852 |
0,478
0,533 0.587 0,653 0,728 |
0,540
0,595 0.669 0,753 0,810 |
0.602
0,657 0,751 0,817 0,892 |
||
| 0.710
0090 0060 1,000 1.120 1.250 1,400 1,600 |
0.007
0,008 6000 010.0 0,011 0.013 0,014 0,016 |
0.790
0.885 0660 1.095 1,218 1,350 1,503 1,707 |
0.856
0,963 1.070 1.176 1,310 1,443 1,597 1,802 |
0.938 | 0,814
0,911 1,018 1,124 1,248 1,381 1,535 1,740 |
0,896
1,013 1.120 1,226 1,370 1,503 1,657 1,862 |
0.978 | ||
Dimensions of enameled wires for grade FIW 4,6,8
| Nominal
conductor diameter |
Conductor
tolerance |
Minimum overall diameter
mm |
Maximum overall diameter
mm |
||||
| mm | 1mm | Grade of
FIW 4 |
Grade of
FIW 6 |
Grade of
FIW 8 |
Grade of
FIW 4 |
Grade of
FIW 6 |
Grade of
FIW 8 |
| 0.040
0,045 0.050 0,056 0,063 0,071 0,080 060.0 |
0.003
0,003 0.003 |
690.0
0,067 0.073 0,082 0600 0,098 0,109 0.121 |
0800
0600 S600 0,105 0.116 0,124 0,137 0.149 |
0,100
0,112 0,117 0.129 0,142 0,150 0,165 0,177 |
690’0
0.078 C8o.0 0,092 0,102 0,110 0,122 0,134 |
0,089
0,100 0,105 0,116 0.128 0,136 0,150 0.162 |
0,109
0,122 0,127 0,140 0,154 0,162 0,178 0.190 |
| 1,000
1.120 1,250 1,400 1,600 |
0,010
0,011 0,013 0,014 0,016 |
1.125
1,249 1,382 1,536 1,741 |
1,227 | 1,175
1,309 1,442 1,596 1,801 |
1,277 | ||
| Nominal conductor
diameter mm |
Resistance
0/m |
|
| Minimum | Maximum | |
| 0,040
0,045 0,050 0,056 0.063 |
12,280
9,705 7,922 6,316 5,045 |
14,920
11,790 9,489 7,565 5,922 |
| NOTE 1 The limit values shown in Table 3 are derived from calculations madeaccording to IEC 60317-0-1:2013, Annex B.NOTE 2 For the nominal resistance,see IEC 60317-0-1:2013,Annex C. | ||
| Nominal conductor
diameter mm |
Minimum elongation at
break % |
| 0,040
0,045 0900 0.056 0.063 0.071 0900 0600 |
9
9 10 10 12 13 14 15 |
| 1,000
1.120 1,250 1,400 1,600 |
30
30 31 32 32 |
Springiness for grades FIW 3,5.7,9
| Nominal conductor
diameter mm |
Mandrel
diameter mm |
Tension
N |
Maximum springback | |||
| Grade of
FIW 3 |
Grade of
FIW 5 |
Grade of
FIW 7 |
Grade of
FIW 9 |
|||
| 080.0
0600 0,100 |
5.0 | 0.25 | 100
94 90 |
N/A
N/A N/A |
N/A
N/A N/A |
N/A
N/A N/A |
| 0,112
0.125 0.140 |
7.0 | 0.50 | 88
84 79 |
N/A
N/A N/A |
N/A
N/A N/A |
N/A
N/A N/A |
| 0,160
0.180 0,200 |
10.0 | 1.00 | 7
75 72 |
N/A
N/A N/A |
N/A
N/A N/A |
N/A
N/A N/A |
| 0,224
0,250 0,280 |
12.5 | 002 | 68
65 61 |
N/A
N/A N/A |
N/A
N/A N/A |
N/A
N/A N/A |
| 0,315
0,355 0,400 |
19.0 | 4.00 | 62
59 55 |
N/A
N/A V/N |
N/A
N/A N/A |
N/A
N/A |
| 0,450
0,500 099.0 |
25.0 | 8.00 | 53
51 48 |
N/A
73 68 |
N/A
06 88 |
|
| 0,630
012.0 008.0 |
37.5 | 12.00 | 53
50 46 |
75
71 65 |
N/A
N/A |
|
| 0060
1,000 1.120 1,250 1,400 009.7 |
50.0 | 15.00 | 51
47 43 39 36 32 |
96
90 84 78 72 65 |
||
Springiness for grades FIW 4,6,8
| Nominal
conductor diameter mm |
Mandrel
diameter mm |
Tension
N |
Maximum springback | ||
| Grade of
FIW 4 |
Grade of
FIW 6 |
Grade of
FIW 8 |
|||
| 090’0
0600 |
5.0 | 0.25 | N/A
N/A |
N/A
N/A |
N/A
N/A |
| 1,000
1.120 1,250 1,400 1,600 |
0.09 | 15.00 | 65
60 54 50 45 |
N/A | |
Mandrel diameters for mandrel winding test for grade FIW 3,5,7 and 9
| Nominal conductor
diameter mm |
Grade of FIW 3 | 0%elongation before winding | ||||
| Grade of
FIW 5 |
Grade of | Grade of
FIW 9 |
||||
| Over | Up to and
Including |
Elongation
before winding % |
Mandrel
diameter mm |
Mandrel
diameter mm |
Mandrel
diameter mm |
Mandrel
diameter mm |
| 090.0
C90.0 0800 0600 0,140 0,200 0,355 0,450 0,710 006 0 1,000 |
0,050
0.063 0,080 060 0 0,140 0,200 0,355 0,450 0,710 0,900 0000 1,600 |
20
15* 10 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
0,150
0.150 0,150 0,150 0,150 8 8 8 8 8 8 |
0020
0020 0,200 000.0 0,300 1-■ 1- 1x■ 3x 3x 3x■ 3x■ |
0,200
0,200 0,200 000.0 0,300 2- 2- 2x■ 4x■ |
–
0,200 000.0 000.0 3x 3x |
| Or to the breaking point of the copper conductor,whichever is less.
· df is thenominal diameter of the wire. |
||||||
Mandrel diameters for mandrel winding test for grade FIW 4, 6 and 8, nominal conductor diameters up to and including 0,090 mm and over 0,900 mm
| Nominal conductor diameter | Grade of FIW 4 | 0%elongation before winding | |||
| mm | Grade of FIW 6 | Grade of FIW 8 | |||
| Over | Up to and
including |
Elongation
before winding % |
Mandrel
diameter mm |
Mandrel
diameter mm |
Mandrel
diameter mm |
| 0,050
C900 0.080 |
0.050
0.063 080.0 060 0 |
10
10 S 0 |
0,200
0,200 0.200 0,300 |
0,200
0.200 0,200 0000 |
0,200
0.200 0.200 0,300 |
| 0060
1,000 |
1,000
1,600 |
0
0 |
2x■
8-2 |
4x
– |
– |
| Or to the breaking point of the copper conductor,whichever is less.
d is the nominal diameter of the wire. |
|||||
Heat shock for grades FIW 3, 5, 7 and 9
| Nominal conductor
diameter mm |
Mandrel diameter
mm |
|||
| Overall diameter range | ||||
| Grade of
FIW 3 |
Grade of
FIW 5 |
Grade of | Grade of
FIW 9 |
|
| 0,160
0,180 0,200 0,224 0,250 |
0,250
0,280 0.315 0,355 0,400 |
0,450
0.450 0,450 0690 0,630 |
0,560
0,560 0990 0080 0,800 |
0,560
0.560 0.560 0001 0001 |
| 0.280
0,315 0,355 0,400 0,450 009.0 |
0090
0,710 0,800 0060 000.1 1.120 |
0090
1,000 1,000 1,000 1.120 1.120 |
0080
1,250 1,250 1,250 0002 0000 |
1,000
1.600 0091 |
| 0,560
0,630 0,710 0,800 0060 |
1,250
1,400 0091 1,800 0002 |
1,400
2,000 000.0 3,550 5,000 |
0002
2,800 2,800 |
|
| 1,000
1.120 1,250 1,400 1,600 |
2,240
3,550 4,000 4,500 5,000 |
0000
0009 5,000 5,600 6,300 |
||
Heat shock for grades FIW 4, 6 and 8
| Nominal conductor
diameter mm |
Mandrel diameter
mm |
||
| Overall diameter range | |||
| Grade of FIW 4 | Grade of FIW 6 | Grade of FIW 8 | |
| 0001
1,120 1,250 1,400 1,600 |
4,000
0009 0000 4,500 5,000 |
0009
0009 |
|
| Nominal conductor
diameter mm |
Minimum specific breakdown voltage
Vium |
||
| Over | Up to and
Including |
Room temperature | Elevated temperature |
| – | 0.100 | 81 | |
| 006.0 | 0091 | 47 | 33 |
| NOTE The specific breakdown voltage is the result of the quotient of the measuredbreakdown voltage and enamel increase. | |||
Application Areas
Fully insulated (FIW) defect-free enameled round copper wire that meets the IEC 60317-0-7 standard is widely used in various types of electrical and electronic equipment, such as:




IEC 60317-0-7:2020 standard provides detailed technical specifications for the manufacture and performance of fully insulated (FIW) defect-free enameled round copper wire. By complying with these strict standards, manufacturers can produce high-quality, high-reliability enameled wires to meet the needs of various types of electrical and electronic equipment. This not only improves the market competitiveness of the product, but also ensures the safety and satisfaction of the end user. In the electrical and electronic fields, fully insulated enameled wires that comply with IEC 60317-0-7 are undoubtedly a guarantee of performance and reliability.
