Film-Insulated Magnet Wire
Film-insulated magnet wire, also known as magnet wire or winding wire, is a type of electrical wire used in various applications where the wire is wound into coils to create electromagnets, transformers, inductors, and other electrical devices.
Build: The increase in wire dimension (diameter, thickness, width) due to the insulation. The formulas defining minimum increases in wire dimension due to the insulation for the following builds are provided in this table.
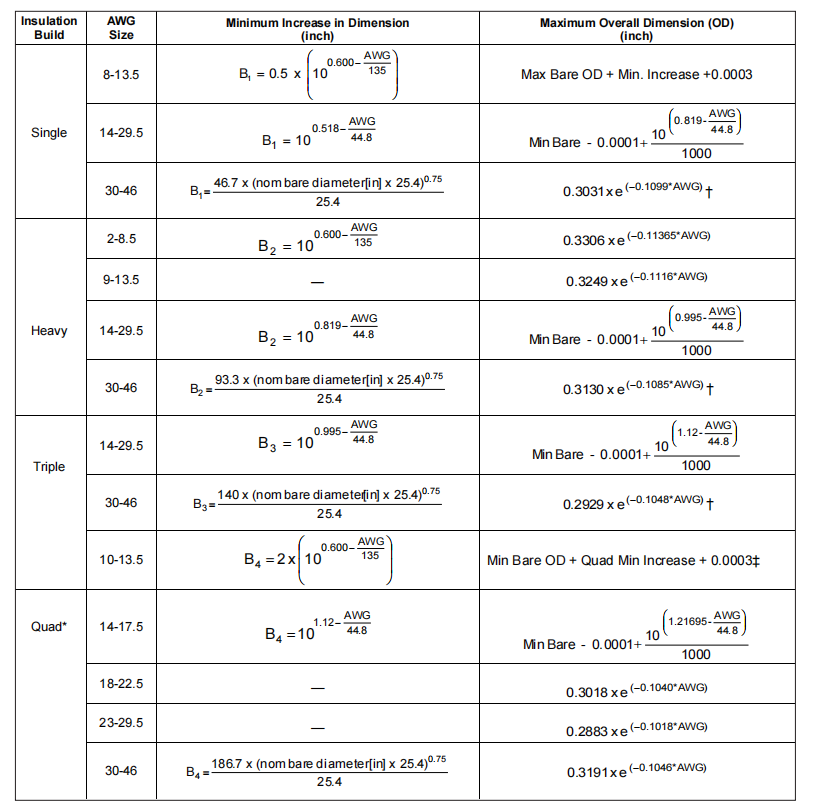
† Applies to 30–44.5 AWG only
‡ Theoretical Minimum Quintuple Build increase
* Not applicable to MW 16-C Quad
Single Build: A reference terminology denoting the lowest of four Standard NEMA film builds.
heavy build: A reference terminology denoting Standard NEMA film builds, which are approximately two times the increases specified for single builds.
Triple Build: A reference terminology denoting Standard NEMA film builds, which are approximately three times the increases specified for single builds.
Quadruple Build: A reference terminology denoting Standard NEMA film builds, which are approximately four times the increases specified for single builds.
Type 1 Self-bonding: A single build insulated magnet wire with a self-bonding outer coating. The maximum overall diameter does not exceed the maximum overall diameter of heavy build.
Type 2 Self-Bonding: A heavy build insulated magnet wire with a self-bonding outer coating. The maximum overall diameter does not exceed the maximum overall diameter of triple build.
Type 3 Self-Bonding: A triple build insulated magnet wire with a self-bonding outer coating. The maximum overall diameter does not exceed the maximum overall diameter of quadruple build.
Conductor: A substance used to transmit electrical current.
Covering: A fibrous or tape insulating material that is wound, wrapped, or braided around a bare or film-coated conductor.
Crack In Film Coating: An opening in the coating that exposes the bare conductor to view at the magnification specified in Part 3.
Degree Of Overlap: Percentage of the tape width covered by subsequent tape layers applied during the wrapping process.
Film Coating: A continuous barrier of polymeric insulation.
Film-Insulated Wire: A film-coated conductor.
Full Rounded Edge: An edge with corner radii that are essentially half the thickness of the wire.
Insulation: A dielectric medium that is applied to the conductor.
Magnet Wire: An insulated wire used primarily for the winding of coils in order to provide an electromagnetic field (also known as winding wire).
Number Of Layers: The equivalent number of coverings resulting from the number of tapes applied and the percentage of overlap used during the wrapping process.
Number Of Tapes: The count of different paper or polyimide tapes applied.
Rectangular Wire: For purposes of this Standard, a wire in which the nominal width and nominal thickness are not equal.
Rectangular Wire—Thickness: The smaller dimension of a bare or insulated rectangular wire.
Rectangular Wire—Width: The larger dimension of a bare or insulated rectangular wire.
Rounded corner: an edge with corner radii that are less than one half the thickness of the wire.
Rounded Edge: an edge with corner radii that are larger than one half the thickness of the wire.
Self-Bonding Overcoat: A material that is applied as an outer coating to insulated wire that, when activated, serves as a bonding agent.
Square Wire: For purposes of this Standard, a wire in which the nominal width and nominal thickness are equal.
Varnish: a liquid resin system that forms a dry, tack-free coating.
NOTE—Electrical insulating varnishes mechanically bond, and provide additional electrical insulation to electrical and electronic equipment.
