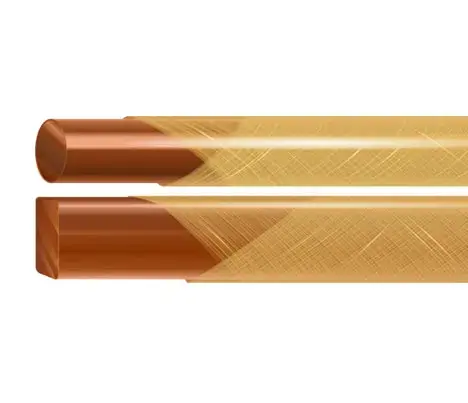
Introduction to Thermoplastic Plastic Films
Thermoplastic film is a film made of thermoplastic resin as the base material. Such as polypropylene film, polypropylene film, polyvinyl chloride film, polystyrene film, polycool film, polyamide film, etc.
Its properties and uses vary with varieties. Polyethylene film and polyvinyl chloride film are used in the largest amount, and they are mainly used in packaging and agriculture; polyamide film and polyamide film are mainly used as insulating materials and packaging materials. The production methods are mostly extrusion blow molding and calendering, extrusion stretching and casting. Thermoplastic film can also be used for enameled wire, which has good insulation and heat resistance.