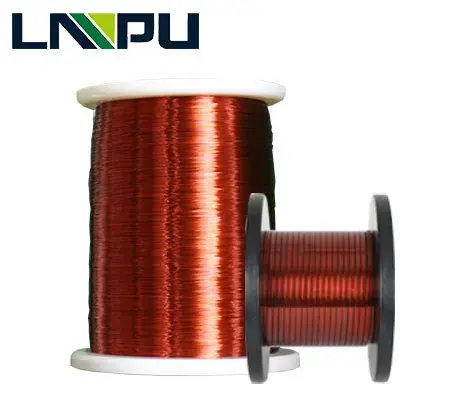
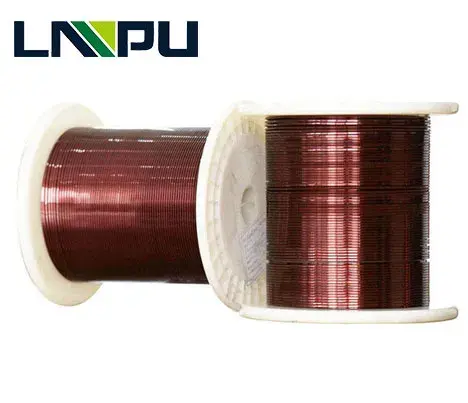
The Types And Uses Of Enameled Copper Wire
| Thermal Class | Types of enameled copper wire | Abbreviation | International abbreviation | Uses or Applications |
| 105℃, 120℃ | Polyvinyl Acetal enameled wire | PVF | Widely used in oil-immersed transformers due to its excellent high temperature hydrolysis resistance, especially acetal enameled flat wires are used to make Transposed wires, used in large transformers. | |
| 130℃, 155℃ | Polyester enameled wire | QZ | PEW | Electronic communication lighting coils, sealed submersible motors, micro generators, heat-resistant transformers, contactors, solenoid valves |
| 130℃ | Polyurethane enameled wire | QA | UEW | Relays, micromotors, small transformers, degaussing coils, ignition coils, water stop valves, magnetic heads, wires for communication equipment |
| 130, 155 | Polyurethane self-adhesive enameled wire | QAN | SBUEW | Instrument electrical windings, micromotors, small motors, microwave ovens, electromagnetic stoves, disk motors, automobile motors and electromagnetic flowmeters, etc. |
| 180 | Polyesterimide enameled wire | QZY | EIW | Electronics, electricians, electrical equipment, heat-resistant transformers |
| 200 | Polyesterimide/amideimide enameled wire | Q(ZY/ XY ) | EI/AIW | Widely used in refrigerator compressors, air conditioning compressors, power tools, explosion-proof motors and motors and electrical appliances used under high temperature, high cold, radiation resistance, overload and other conditions. |
| 220 | Polyimide enameled wire | Q Y | PIWC | Uses in windings of motors, electrical appliances, instruments, power tools, dry-type power transformers, etc. that require high heat resistance. |
| 240 | Aromatic polyimide enameled wire | Q Y(F) | / | Nuclear power, military industry |
LP Industry Supply the sizes of enameled copper wire
| Name | Enameled Copper Winding Wire |
| Conductor | 99.99% pure Copper |
| Dimension | Round type 0.016-7mm; Rectangular: A> 0.3-10mm, B> 1-22mm; Square: 0.45*0.45mm-6*6mm |
| Thermal Class | 120(Class E), 180(Class H), 200(Class C), 220(Class C+),240(Class HC) |
| Insulation Thickness: | G1; G2 or single build; heavy build; Self-bonding |
| Standard | IEC 60317-16,60317-16/28,MW36 60317-29 BS6811,MW18 60317-18 ,MW20 60317-47 |
| Certificate | UL |
| Packing | 30kg-150kg ply-wood spool(250*400 / 250*500/ 250*600/ 250*730) |
IEC60317 Dimensions of enamelled wires – Preferred nominal conductor diameters
| Nominal conductor diameter (mm) | Conductor tolerance ±(mm) | Minimum increase due to the insulation(mm) | Maximum overall diameter(mm) | ||||
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | ||
| 0.018
0.020 0.022 0.025 0.028 0.032 0.036 0.040 0.045 0.050 0.056 0.063 0.071 0.080 0.090 0.100 0.112 0.125 0.140 0.160 0.180 0.200 0.224 0.250 0.280 0.315 0.355 0.400 0.450 0.500 0.560 0.630 0.710 0.800 0.900 1.000 1.120 1.250 1.400 1.600 1.800 2.000 2.240 2.500 2.800 3.150 3.550 4.000 4.500 5.000 |
0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.006 0.006 0.007 0.008 0.009 0.010 0.011 0.013 0.014 0.016 0.018 0.020 0.022 0.025 0.028 0.032 0.036 0.040 0.045 0.050 |
0.002
0.002 0.002 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.004 0.004 0.005 0.005 0.006 0.006 0.007 0.007 0.008 0.008 0.009 0.010 0.011 0.012 0.013 0.014 0.015 0.017 0.018 0.019 0.020 0.021 0.022 0.024 0.025 0.027 0.028 0.030 0.032 0.034 0.034 0.035 0.036 0.038 0.039 0.040 0.041 0.042 0.043 0.045 0.046 0.047 0.049 0.050 |
0.004
0.004 0.005 0.005 0.006 0.007 0.008 0.008 0.009 0.010 0.011 0.012 0.012 0.014 0.015 0.016 0.017 0.019 0.021 0.023 0.025 0.027 0.029 0.032 0.033 0.035 0.038 0.040 0.042 0.045 0.047 0.050 0.053 0.056 0.060 0.063 0.065 0.067 0.069 0.071 0.073 0.075 0.077 0.079 0.081 0.084 0.086 0.089 0.092 0.094 |
0.006
0.007 0.008 0.008 0.009 0.010 0.011 0.012 0.013 0.014 0.015 0.017 0.018 0.020 0.022 0.023 0.026 0.028 0.030 0.033 0.036 0.039 0.043 0.048 0.050 0.053 0.057 0.060 0.064 0.067 0.071 0.075 0.080 0.085 0.090 0.095 0.098 0.100 0.103 0.107 0.110 0.113 0.116 0.119 0.123 0.127 0.130 0.134 0.138 0.142 |
0.022
0.024 0.027 0.031 0.034 0.039 0.044 0.049 0.055 0.060 0.067 0.076 0.084 0.094 0.105 0.117 0.130 0.144 0.160 0.182 0.204 0.226 0.252 0.281 0.312 0.349 0.392 0.439 0.491 0.544 0.606 0.679 0.762 0.855 0.959 1.062 1.184 1.316 1.468 1.670 1.872 2.074 2.316 2.578 2.880 3.233 3.635 4.088 4.591 5.093 |
0.024
0.027 0.030 0.034 0.038 0.043 0.049 0.054 0.061 0.066 0.074 0.083 0.091 0.101 0.113 0.125 0.139 0.154 0.171 0.194 0.217 0.239 0.266 0.297 0.329 0.367 0.411 0.459 0.513 0.566 0.630 0.704 0.789 0.884 0.989 1.094 1.217 1.349 1.502 1.706 1.909 2.112 2.355 2.618 2.922 3.276 3.679 4.133 4.637 5.141 |
0.026
0.030 0.033 0.037 0.042 0.047 0.053 0.058 0.066 0.072 0.081 060.0 0.098 0.108 0.120 0.132 0.147 0.163 0.181 0.205 0.229 0.252 0.280 0.312 0.345 0.384 0.428 0.478 0.533 0.587 0.653 0.728 0.814 0.911 1.018 1.124 1.248 1.381 1.535 1.740 1.944 2.148 2.392 2.656 2.961 3.316 3.721 4.176 4.681 5.186 |
IEC60317 Dimensions of enamelled wires with a bonding layer – Preferred nominal conductor diameters
| Nominal conductor diameter mm | Conductor tolerance ± mm | Minimum increase underlying coating mm | Minimum Increase bonding layer mm | Maximum overall diameter mm | ||
| Grade 1B | Grade 2B | Grade 1B | Grade 2B | |||
| 0.020
0.022 0.025 0.028 0.032 0.036 0.040 0.045 0.050 0.056 0.063 0.071 0.080 0.090 0.100 0.112 0.125 0.140 0.160 0.180 0.200 0.224 0.250 0.280 0.315 0.355 0.400 0.450 0.500 0.560 0.630 0.710 0.800 0.900 1.000 1.120 1.250 1.400 1.600 1.800 2.000 |
0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.006 0.006 0.007 0.008 0.009 0.010 0.011 0.013 0.014 0.016 0.018 0.020 |
0.002
0.002 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.004 0.004 0.005 0.005 0.006 0.006 0.007 0.007 0.008 0.008 0.009 0.010 0.011 0.012 0.013 0.014 0.015 0.017 0.018 0.019 0.020 0.021 0.022 0.024 0.025 0.027 0.028 0.030 0.032 0.034 0.034 0.035 0.036 0.038 0.039 0.040 |
0.004
0.005 0.005 0.006 0.007 0.008 0.008 0.009 0.010 0.011 0.012 0.012 0.014 0.015 0.016 0.017 0.019 0.021 0.023 0.025 0.027 0.029 0.032 0.033 0.035 0.038 0.040 0.042 0.045 0.047 0.050 0.053 0.056 0.060 0.063 0.065 0.067 0.069 0.071 0.073 0.075 |
0.002
0.002 0.002 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.003 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.008 0.009 0.010 0.010 0.010 0.011 0.012 0.013 0.013 0.014 0.015 0.016 0.016 0.017 0.017 0.018 0.019 0.020 0.020 0.021 0.022 0.022 0.023 0.023 0.024 0.025 |
0.026
0.030 0.034 0.038 0.044 0.050 0.055 0.062 0.068 0.075 0.085 0.094 0.105 0.117 0.129 0.143 0.158 0.175 0.197 0.220 0.243 0.270 0.300 0.331 0.369 0.413 0.461 0.514 0.568 0.630 0.704 0.788 0.882 0.987 1.091 1.214 1.346 1.499 1.702 1.905 2.108 |
0.029
0.033 0.037 0.042 0.048 0.055 0.060 0.068 0.074 0.082 0.092 0.101 0.112 0.125 0.137 0.152 0.168 0.186 0.209 0.233 0.256 0.284 0.316 0.348 0.387 0.432 0.481 0.536 0.590 0.654 0.729 0.815 0.911 1.017 1.123 1.247 1.379 1.533 1.738 1.942 2.146 |
Manufacturing Process of Enameled Copper Wire
1. Material Preparation
- Selection of Raw Material: High-purity copper or aluminum is chosen as the base material for its excellent electrical conductivity.
- Casting and Rolling: The raw metal is cast into rods or bars, which are then rolled into the desired flat or rectangular cross-section.
2. Drawing
- Initial Drawing: The metal is drawn through a series of dies to reduce its cross-sectional area while maintaining the flat shape. This process can involve multiple stages to achieve the required dimensions.
3. Annealing
- Heat Treatment: The drawn wire is subjected to annealing, a heat treatment process that softens the metal, relieving internal stresses and enhancing its ductility and workability.
4. Cleaning
- Surface Cleaning: The wire is thoroughly cleaned to remove any oxides, lubricants, or contaminants from its surface. This step is crucial to ensure proper adhesion of the enamel coating.
- Chemical Cleaning: Often involves an acid bath or similar chemical treatment.
- Mechanical Cleaning: May include brushing or abrasive techniques.
5. Enameling
- Coating Application: The cleaned wire is passed through an enameling machine where it is coated with a layer of insulating enamel.
- Dipping or Spraying: The wire may be dipped into the enamel solution or have the enamel sprayed onto it.
- Multiple Coatings: Multiple layers of enamel may be applied, with each layer being cured before the next one is applied.
6. Curing
- Heat Treatment: After each enamel application, the wire is passed through an oven or furnace where the enamel is cured. This process involves heating the wire to a specific temperature to harden and stabilize the enamel coating.
- Controlled Environment: The curing environment is carefully controlled to ensure consistent and defect-free coatings.
7. Quality Control
- Inspection and Testing: The enameled wire undergoes rigorous inspection and testing to ensure it meets all specified standards and requirements.
- Dimensional Checks: Verifying the width, thickness, and overall dimensions of the wire.
- Electrical Testing: Ensuring proper insulation resistance and dielectric strength of the enamel coating.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing the flexibility, adhesion, and durability of the enamel.
8. Spooling and Packaging
- Spooling: The finished enameled flat wire is wound onto spools or reels in preparation for storage or shipment.
- Packaging: The spools are then packaged securely to protect the wire during transportation and storage.
9. Final Inspection
- Random Sampling: Samples from each batch are taken for final quality assurance tests to ensure consistency and reliability of the product.
LP Industry has the lastest advanced winding machine for enameled wire, take up machine, baking machine, extruding machine, drawing machine and testing equipment, etc. Testing equipment has computer conductor resistance tester, tensile testing machine, solderability tester, tangent delta tester, thermal cut-through tester, elongation tester, automatic voltage tester, automatic rebound tester. Customers can buy the enameled copper wire with directly factory price from LP Industry, and clients can also custom AWG and SWG enameled copper wire, Max. size of round enameled copper wire is 7mm, the Max. size square copper wire is 6mm*6mm, flat wire is needed the size from clients’ requirements.